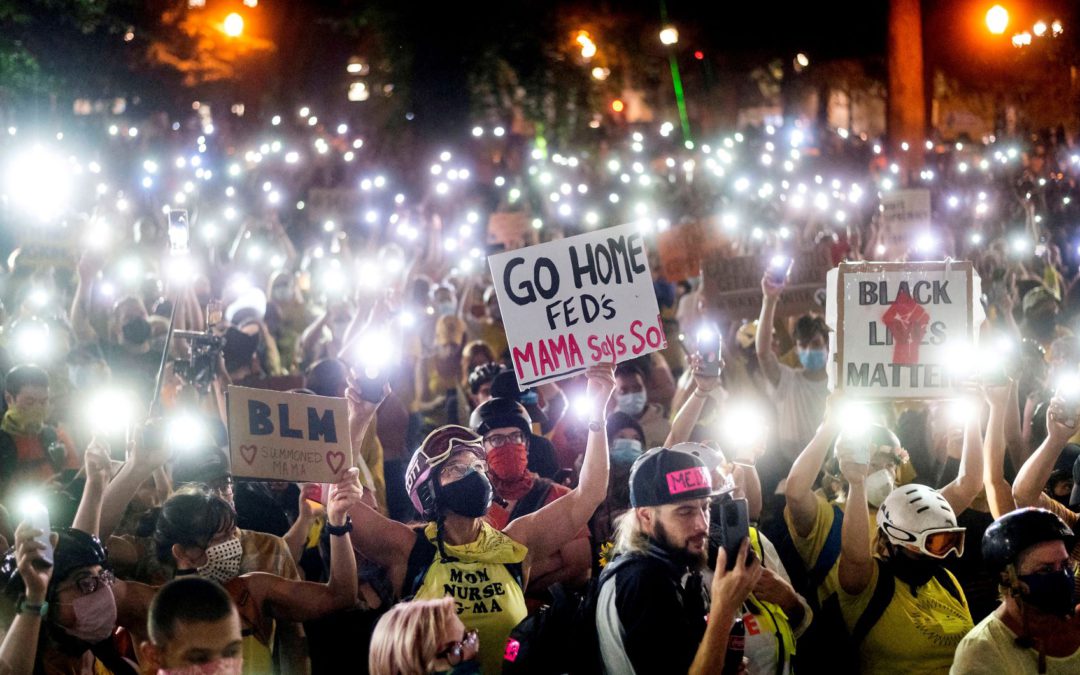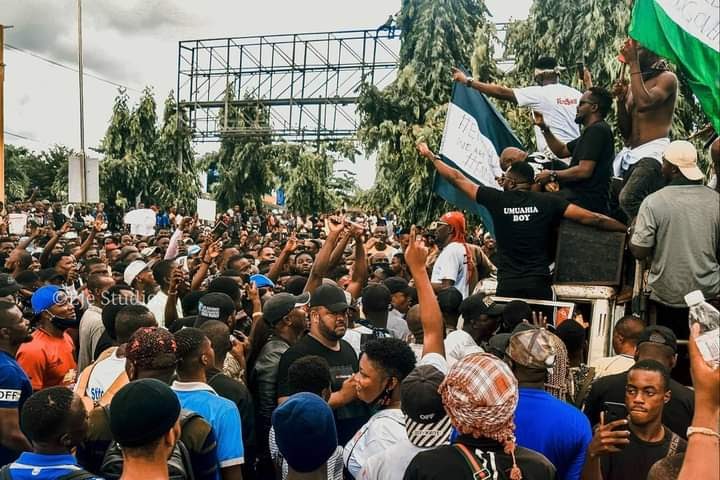by Li Keira Yin | 25 Mar 2021 | Americas, Educators' Catalog, Environment, Health and Wellness, Student Posts, Thacher School, Youth Voices
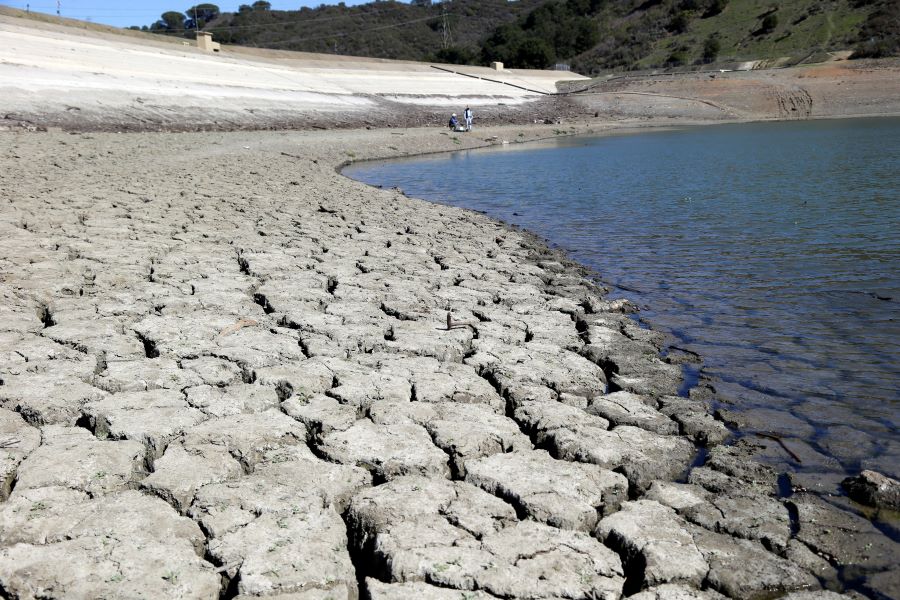
California’s water supplies are being squeezed by climate change. By better capturing, recycling and distributing water, the state can avert a crisis. A dry reservoir bed in Cupertino, California, 13 March 2014 (AP Photo/Marcio Jose Sanchez) Water has long been...
Beset by raging wildfires and drought, Californians could be forgiven for thinking a climate Armageddon is upon them. The easy assumption would be that global warming means the most populous U.S. state does not have enough water for its many farmers and citizens. Keira Yin of The Thacher School provides a fuller picture by interviewing a water resilience expert and probing data. She concludes that stepped-up efforts to better capture, recycle and distribute water could go a long way towards ensuring the state can fend off the effects of climate change. Ask your students to consider how climate change is affecting water supplies in your region and to identify what the government is or could be doing about it.

by Santiago Riveros Crosby | 16 Mar 2021 | Educators' Catalog, Environment, Gimnasio Los Caobos, Student Posts, Youth Voices
An old man and his great-grandson look out over a city—devoid of trees. Is this nature as our offspring will know it? Claude Monet, “Weeping Willow” (1918), Columbus Museum of Art, Wikimedia Commons Santiago Riveros Crosby is a student at News Decoder...
Climate change poses an existential threat to humanity that hangs like a dark cloud over students. Add to that a pandemic that has killed millions and turned students’ lives inside out, and you have a one-two punch to the mental well-being of even the most resilient students. Santiago Riveros Crosby of Gimnasio Los Caobos has both climate change and COVID-19 in mind in his very short story that takes us to the year 2060 and a landscape devoid of trees, viewed by a masked boy and his great-grandfather. Writing tightly is tough, but in just a few words, Crosby evokes a young generation’s angst. Ask your students to express their feelings about global warming and the pandemic — using the medium of their choice.

by Lucy Jaffee | 24 Feb 2021 | Americas, Climate change, Contest winners, Contests, Educators' Catalog, Environment, La Jolla Country Day School, Student Posts, United States, Youth Voices
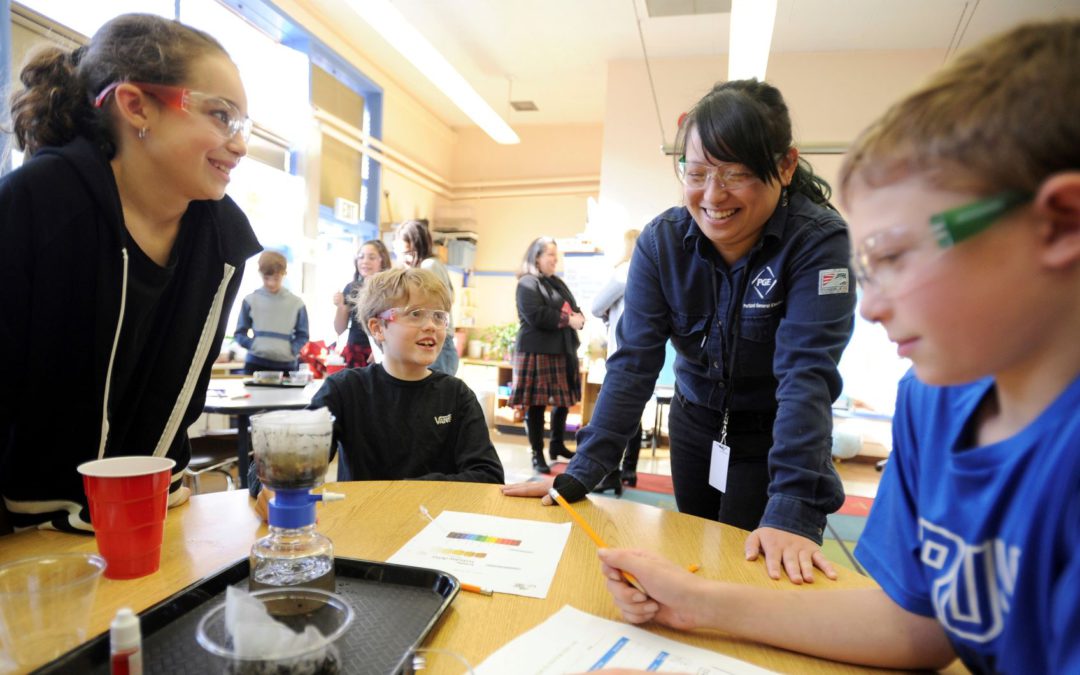
Most Americans want schools to teach about global warming. But skeptics and lack of teacher training make it hard to implement climate change education. Students learn about water filtration as part of their climate literacy curriculum in Portland, Oregon, 30 January...
Climate deniers have lost the political high ground in the United States, but the struggle to combat global warming has only just begun. Lucy Jaffee of La Jolla Country Day School explores why teaching about climate change can help reduce carbon emissions, but also why U.S. schools are having such a hard time fostering climate literacy. She interviewed a local expert and two teachers in her examination of the challenges schools face in meeting the expectations of parents who want climate change in the curriculum. Ask your students to explore how climate change is being taught in their school, and if not, why not?
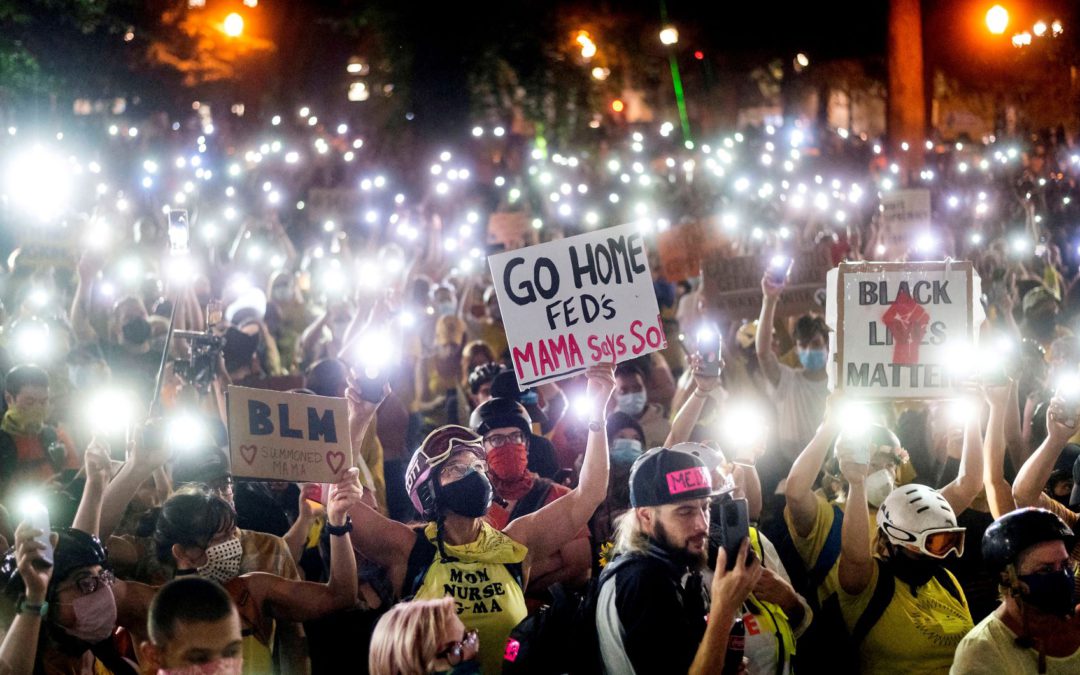
by Christina MacCorkle | 26 Jan 2021 | Americas, Asia, Contest winners, Contests, Donald Trump, Educators' Catalog, Future of Democracy, Human Rights, Joe Biden, Politics, Student Posts, Thacher School, Youth Voices
A pro-democracy movement in South Korea offers lessons to two U.S. social movements — against police brutality and for a defeated ex-president. Black Lives Matter protesters hold their phones aloft in Portland, Oregon, 20 July 2020. (AP Photo/Noah Berger) This story...
Sociologists are the first to admit they are apt to speak their own tongue, so reporting on sociological research can tie even experienced reporters in knots. And high school students are not always interested in events of half a century ago. So it’s a rare pleasure when a student connects a pro-democracy movement in South Korea during the 1960s and ‘70s with social movements in the United States today, and renders sociology understandable to the untrained ear in the process. Christina MacCorkle of The Thacher School takes academic research about a country far from her school’s California campus and connects it to current events in the U.S., using simple language to convey complex academic arguments. Many students are trained to write academic essays, but MacCorkle enlightens those of us outside of academia.

by Elena Townsend-Lerdo | 23 Dec 2020 | Contest winners, Contests, Educators' Catalog, Human Rights, Student Posts, Thacher School, United States, Youth Voices
Prisoners run a newspaper from inside a California jail. The monthly raises awareness of social justice issues and offers a new chance to convicts. Jonathan Chiu (Photo by Christie Goshe) This story won a third prize in News Decoder’s Ninth Storytelling Contest....
Elena Towsend-Lerdo introduces us to a convicted murderer who finds redemption at a newspaper run by prisoners in California’s oldest jail. The San Quentin News is online and accessible to readers around the world. Townsend-Lerdo interviews Jonathan Chiu, who was released after serving 16 years of his 50-year sentence, and a journalism professor who trains prisoners, providing first-hand insight into incarceration and rehabilitation. Those are meaty issues, but the student at La Jolla Country Day School avoids sweeping statements to offer us a peek into the U.S. criminal justice system and a unique path to atonement. Who could your students interview to learn about criminal justice?
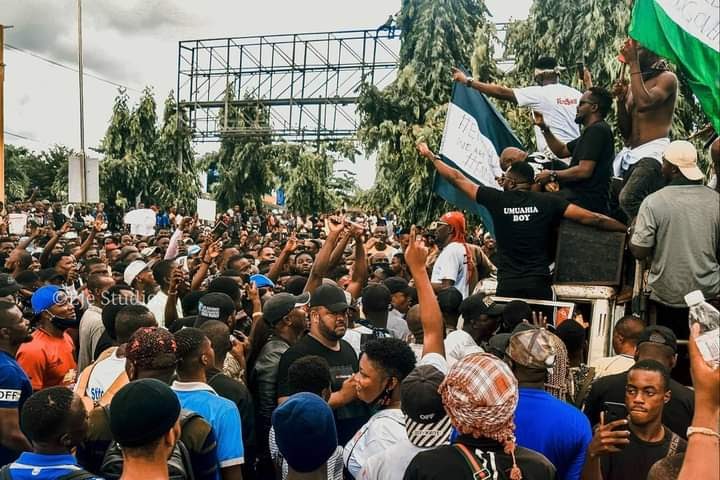
by Joy Chinaza | 9 Dec 2020 | Africa, African Leadership Academy, Contest winners, Educators' Catalog, Eyewitness, Future of Democracy, Human Rights, Personal Reflections, Politics, Student Posts, Youth Voices
I joined protests against police brutality in my home country of Nigeria and saw them almost become a war, then a rude awakening for youth. Protesters in Umuahia, Nigeria, October 2020 (All photos courtesy of Eje Studios) This story was a runner-up in News...
Joy Chinaza takes us into the streets of Nigeria to join young people protesting against police brutality. Like youth elsewhere this year, she is driven by anger over rights abuses perpetrated by police charged with protecting civilians but who instead turn weapons against minorities. A shared sense of injustice motivates Chinaza and millions of others around the globe, making her story a metaphor for youthful outrage. But the personal details in the tale by the African Leadership Academy student, including the beating her own brother suffers, add poignancy that sets her account apart. Make sure students note how the first-person pronoun draws them into the story. And how her outrage — so common among youth — is tinged with ambiguity at the end.

by Jasmine Li | 1 Dec 2020 | China, Discovery, Educators' Catalog, Health and Wellness, Identity, Student Posts, United States, Westover School, Youth Voices
COVID-19 left me in limbo in the United States, full of fear and anger. Then I returned home to China to face criticism before reuniting with my family. An empty John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York (All photos by Jasmine Li) So this is where I am going...
The coronavirus pandemic has put strains on students, their families, schools, entire communities. But Jasmine Li, a Chinese student at Westover School in the United States, provides a first-person account of the special difficulties facing foreign nationals caught in limbo as COVID-19 triggered global travel restrictions. Li cannot return to her temporary home at school, and when she finally makes it home to China, she discovers some compatriots consider her a traitor and urge her to leave. Adolescence can be a difficult period of self-discovery, but Li’s painful experiences are the product of a globalized world that, in normal circumstances, offers extraordinary opportunities but which, during a pandemic, sees forgotten borders re-emerge. Ask each student to describe their most difficult moment during the pandemic. How do their experiences compare?
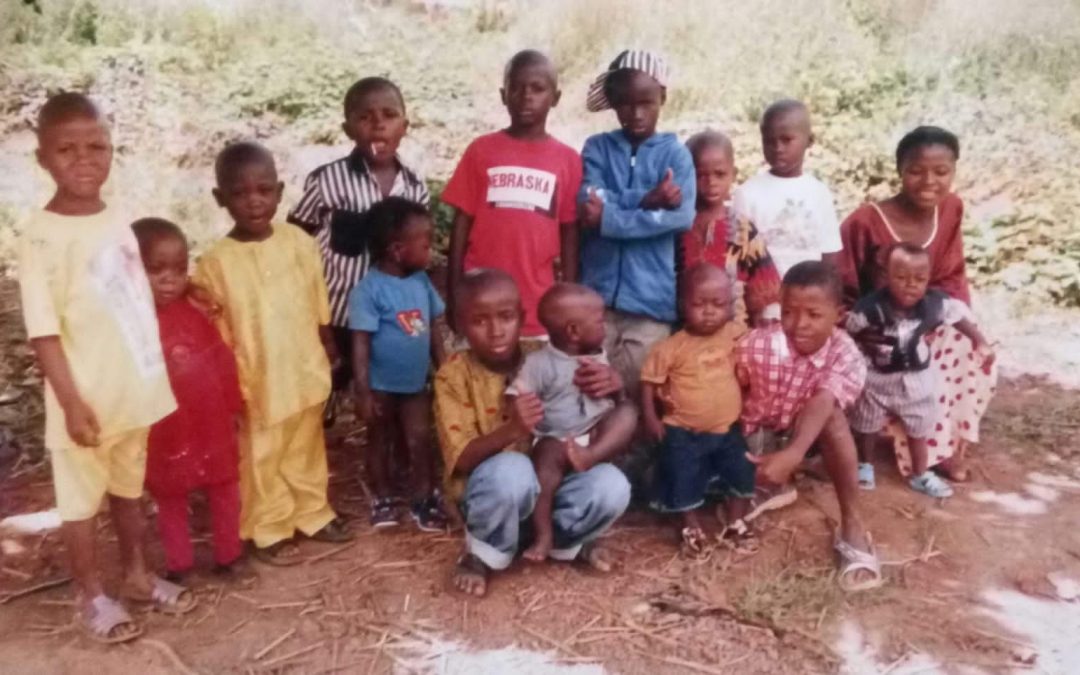

by Varlee S Fofana | 10 Nov 2020 | Africa, African Leadership Academy, Contest winners, Discovery, Educators' Catalog, Identity, Personal Reflections, Refugees, Student Posts, Youth Voices
My family fled civil war in Liberia to a refugee camp in Guinea in West Africa. I learned the power of resilience and the value of diversity. The author, in white next to the woman on the right, at the Kouankan refugee camp in Guinea This story won first prize in News...
News Decoder’s goal is to create a global community, and Varlee Fofana has added his unique voice to the conversation with an essay about growing up in a refugee camp in Guinea. Not many News Decoder students have had to flee civil war as Fofana did, yet many play football, as the author did to connect with other refugee children. Gathering wood, plowing farmland or selling kerosene might not be common chores for most News Decoder students, but they, too, face challenges. Ask your class to read Fofana’s story and then, in up to 600 words, describe a personal experience that shaped their life and character. Encourage them to follow Fofana’s example by using simple words and an unassuming tone to draw readers into their world.
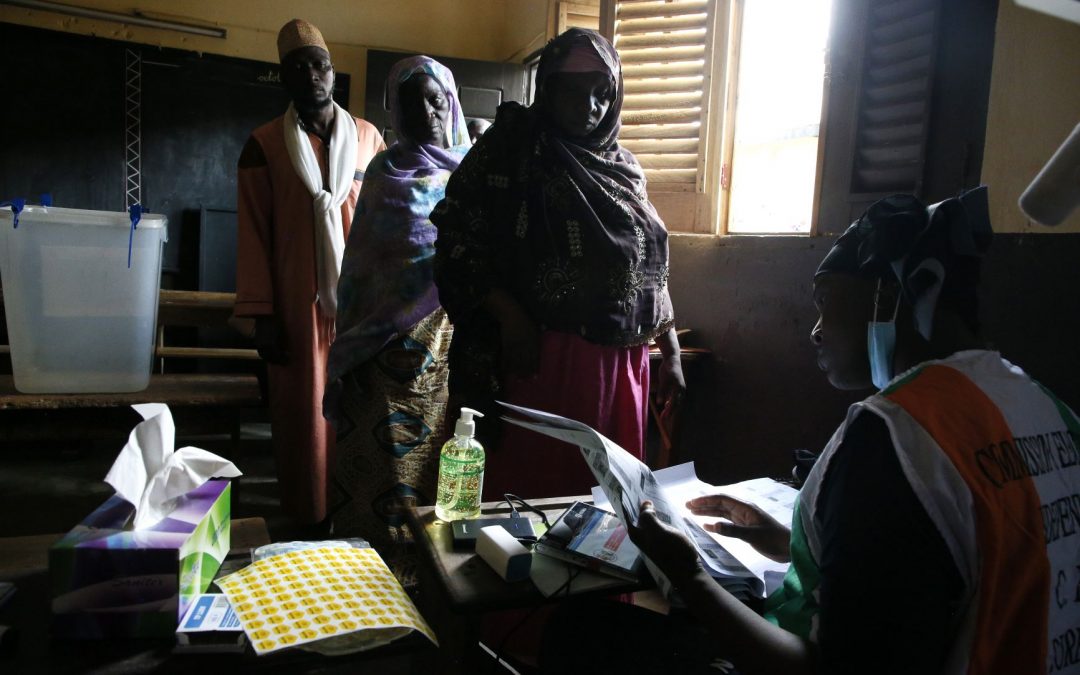

by Adayé Sosthène Yvan N'guettia | 2 Nov 2020 | Africa, African Leadership Academy, Contest winners, Educators' Catalog, Government, Student Posts, Youth Voices
For years, Ivory Coast has been split politically and at times torn by outbursts of violence. Youth are working for peace in the West African nation. Voters at a polling station during the first round of Côte d’Ivoire’s presidential election in Abidjan, 31...
Ivory Coast has a complex political story, but Adayé Sosthène Yvan N’guettia keeps it simple in his story about youth working for peace in the West African nation. Many young people are upset over the state of the world that they will inherit, but N’guettia shows initiative by interviewing three activists toiling for change in Côte d’Ivoire. He listens and offers telling quotes, using a deft hand to drive home his message. Growing up is about discovering the world, and some students — N’guettia among them — see the challenge as a learning adventure. Ask your class to read N’guettia’s story, interview three activists and, using the activists’ words, summarize what they’ve learned.

by Lucy Jaffee | 27 Oct 2020 | Contest winners, Educators' Catalog, Human Rights, La Jolla Country Day School, Student Posts, Youth Voices
A U.S. school district wants the Supreme Court to overturn a landmark free speech case and let it punish a student for criticizing her school online. Students protest for the right to free speech outside the Supreme Court in Washington, DC, 19 March 2007. (AP...
Lucy Jaffee of La Jolla Country Day School tackled a complicated topic — a court case involving a student’s freedom of speech and social media — by interviewing two experts, including the foremost authority on the U.S. First Amendment, Floyd Abrams. The lesson: If you put effort into understanding an issue, experts will be glad to speak to you. Students should contact experts because they will offer unique insights and help answer the question, “What next?”
The case Jaffee’s article focuses on lends itself to classroom discussion because it engages a matter of great interest to students. While students may instinctively side with the young woman whose Snapchat post triggered the controversy, there may be other off-campus outbursts on social media — Holocaust denial, racist language — that they might like to see sanctioned. Like so much in life, First Amendment issues often lie in the gray zone.